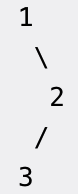题目内容
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
用迭代算法完成
示例
输入: [1,null,2,3]
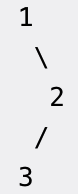
输出: [3,2,1]
题解
本题有多种思路可以求解。
首先,看一个比较取巧的方法。
我们知道,前序遍历的顺序是根、左、右,因此我们可以在前序遍历的基础上,将遍历顺序改为根、右、左,这下这个顺序就是后序遍历的镜像顺序,得到这个顺序后我们反转输出即为后序遍历的顺序。
第二,我们可以采用递归的思想。
具体思路是对左和右子树遍历,然后依次将答案放入,最后放入根的值。
第三,非递归的思想,需要用栈的数据结构,具体为之前提到过的Mirros遍历算法。
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
while(root||stk.size()){
while(root){
res.push_back(root->val);
stk.push(root);
root=root->right;
}
root = stk.top()->left;
stk.pop();
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result, left, right;
if(!root) return result;
left = postorderTraversal(root->left);
for(auto &x:left) result.push_back(x);
right = postorderTraversal(root->right);
for(auto &x:right) result.push_back(x);
result.push_back(root->val);
return result;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<TreeNode*> s;
if(!root)return result;
TreeNode *current = root, *lastVisited = NULL;
while (current != NULL || !s.empty()) {
while (current != NULL) {
s.push(current);
current = current->left;
}
current = s.top();
if (current->right == NULL || current->right == lastVisited) {
s.pop();
result.push_back(current->val);
lastVisited = current;
current = NULL;
} else {
current = current->right;
}
}
return result;
}
};
|